Research Progress of GPCR Antibody Drugs
G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) antibodies have been listed as key targets in the field of antibody drugs. So what exactly is GPCR? What is the current research progress of GPCR antibody drugs? In this article, we will give a detailed introduction about GPCR. As an important class of drug target molecules, GPCR has attracted many attention in the field of drug development, especially in the field of monoclonal antibody drug development. Currently, more and more clinical drug experiments have been extended to antibody drugs targeting GPCR. Human understanding of the biological properties of GPCR in oncology, especially in the field of tumor immunity, has provided broad prospects for the application of therapeutic antibodies to GPCR, whether as monotherapy or combination therapy. The application of new generation protein drug development strategies, such as bispecific antibodies and antibody conjugated drugs, has opened up a new field for the application of antibody drugs.
▍ What is GPCR?
G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) is the largest membrane protein family in the human genome, with a total of more than 800 genes and can be divided into multiple subfamilies.
As shown in the figure below, GPCR is composed of seven α helical structures that span the membrane of the cell.
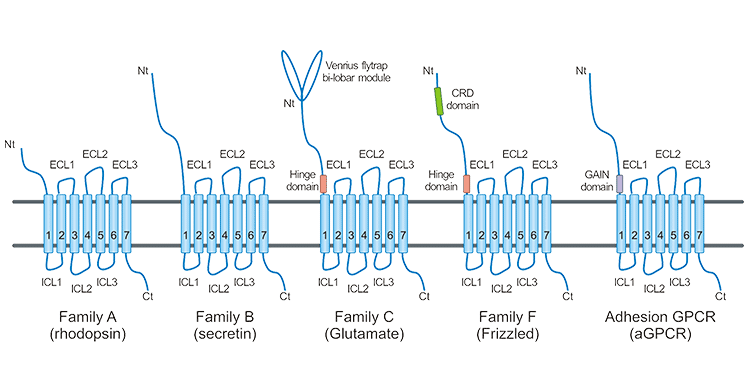
The N-terminal and three loops are located outside the cell, mediating the interaction of acceptor ligands; The C-terminal and three loops are located within the cell, and the C-terminal and third loop play an important role in the interaction between GPCR proteins and downstream G proteins, thereby mediating intracellular signal transduction. The binding of specific ligands to GPCR can cause the activation of G protein, producing a second messenger Ca2+or cAMP, which transmits extracellular signals received by GPCR downstream; However, GPCR can also mediate G protein independent signal transduction, such as through interaction with β- Molecular interactions such as arrestin regulate downstream pathways.
▍ Overview of current research on GPCR related drugs
GPCR is widely distributed in organs and tissues such as the central nervous system, immune system, cardiovascular system, and retina, and participates in the development and normal functioning of the body. Abnormality in the regulation of intracellular signaling pathways associated with it, or the use of exogenous pathogenic factors as receptors to attack body cells, can lead to the occurrence of a series of diseases.
There are about 370 GPCRs candidates as drug targets. Currently, and 476 GPCR drugs approved for marketing by the FDA, of which 92% are small molecule drugs, 5% are polypeptide drugs, and 2% are protein drugs, while only 2 are antibody drugs. (data source: https://gpcrdb.org/)
From the current data, the drugs targeted to GPCR and approved are mainly small molecule drugs, while the reason for the relatively few antibody drugs targeted to GPCR is the difficulty in development. The preparation of GPCR antigen is difficult. Vitro Biotech has developed a number of GPCR protein overexpression CHO cells, which can produce a large number of required proteins from these stable cell lines.
▍ Research progress in GPCR antibody drugs
The GPCR antibody R&D pipelines have developed rapidly with the enhancement of clinical development capabilities. Currently, there are over 170 effective projects targeting 76 GPCR targets. However, there are only 2 approved GPCR targeted monoclonal antibodies. In addition, there are multiple monoclonal antibodies to GPCR that are in clinical phase 1 or phase 2.
1. Mogamulizumab, a monoclonal antibody against CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4) developed by Kyowa Hakko Kirin of Japan, was first approved for marketing in Japan in 2012 and is on sale under the trade name Poteligo. It was approved for marketing by the FDA in 2018. Mogamulizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4), which is often expressed on leukemia cells in certain hematological malignancies, including CTCL. The approved indications for this drug are CCR4 positive adult T-cell leukemia, CCR positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma, and CCR4 positive cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
CCR4 related stable cell lines in Vitro Biotech: CCR4/β-Arrestin/CHO Cell Line, CCR4/Ga15/CHO Cell Line
2. Leronlimab (PRO140) is a humanized immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 monoclonal antibody developed by Progenics Pharmaceuticals Inc. against CC chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5), which has potential activity as a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) entry blocker and potential protective activity against graft versus host disease (GvHD). CCR5 is a co receptor required for HIV cell entry and plays a key role in immune regulation. Leronlimab has been developed and entered different clinical stages (a total of 24 clinical trials) targeting multiple diseases, namely CCR5 eosinophilic HIV infection, metastatic TNBC, metastatic colorectal cancer, non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and graft versus host disease (GvHD). In 2020, Leronlimab was approved to conduct a phase 2b/3 trial of 390 patients with severe COVID-19.
CCR5 related stable cell lines in Vitro Biotech: CCR5/Ga15/CHO Cell Line, CCR5/CHO Cell Line
3. Uluplumab (BMS-936564) is a CXCR4 specific complete human IgG4 (S224P) mAb developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb. CXCR4 is not only expressed on white blood cells, platelets, and other non hematopoietic cells that constitute the tumor matrix microenvironment, but also overexpressed in most human cancers. Together with its endogenous ligand CXCL12, CXCR4 plays a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of cancer, involving proliferation, adhesion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and survival. Ulopulumab has been evaluated in two phase I clinical trials in subjects with various hematological malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), multiple myeloma (MM), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and has shown encouraging results. This antibody is currently in the clinical phase 2 development stage of Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
CXCR4 related stable cell lines in Vitro Biotech: CXCR4/CHO Cell Line
4. Nimacimab (ryi-018) is a type 1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1) drug mainly developed by Bird Rock Bio Inc. It is used for kidney disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, metabolic disorder, fibrosis, diabetes nephropathy, and diabetes gastroparesis. Currently, the highest research and development status is in clinical phase II.
CB1 related stable cell lines in Vitro Biotech: CB1/CHO Cell Line
5. Glutazumab (also known as GMA102 or GMA105) is a new long-acting anti GLP-1R humanized antibody and GLP-1 fragment fusion protein developed by Hongyun Huaning for T2D and obesity, which plays an anti diabetes role by targeting dual receptor binding sites. This antibody proposes another targeting strategy, that is, binding to the function conferred by the antibody through fusion of peptide ligands. Such a structure exhibits superior safety and tolerance to similar GLP1 analogues. The current highest research and development status is in clinical phase II.
GLP-1R related stable cell lines in Vitro Biotech: GLP1R/CRE-Luc/HEK293 Cell Line
6. Avdoralimab (IPH-5401) is a monoclonal antibody developed by Innate Pharma that can specifically bind to C5AR1 expressed on myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC) and neutrophils, blocking the binding of C5a to C5aR1. Originally used in clinical development of rheumatoid arthritis in Australia. However, IPH-5401 is currently conducting a phase 1/phase 2 joint study (NCT03665129) and checkpoint inhibitor Durvalumab (anti PD-L1) in the context of immunooncology to treat patients with selected solid tumors (NSCLC, HCC, RCC, urothelial cell carcinoma). The current highest research and development status of this monoclonal antibody is in clinical phase II.
C5AR1 related stable cell lines in Vitro Biotech: C5aR1/β-Arrestin/CHO Cell Line, C5aR1/CHO Cell Line
7. Plozalizumab (MLN-1202) is a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against human chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) developed by Takeda Oncology. When pluzalizumab binds to CCR2 and prevents endothelial derived CLL2 (monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 or MCP1) from binding to its receptor CCR2, it may inhibit the activation of CCR2, thereby inhibiting angiogenesis, tumor cell migration, and tumor cell proliferation. In addition, this drug may reduce C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Although the antibody drug has entered the second phase of research on multiple disease indications, two clinical phase II test items for diabetes nephropathy (NCT02410499) and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (NCT0238971) have been canceled. The current highest research and development status of this antibody drug is in clinical phase II.
CCR2 related stable cell lines in Vitro Biotech: CCR2/Ga16/HEK293 Cell Line, CCR2/Ga15/CHO Cell Line, CCR2/CHO Cell Line
8. Volagidemab (REMD-477) is a human anti-glucagon receptor antibody developed by Kexin Meide for adolescents with type I diabetes (T1D) and type II diabetes (T2D). Its mechanism of action is to increase hepatic glucose uptake by blocking the glucagon receptor (GCGR) signal transmission, reduce hepatic glycogen decomposition and gluconeogenesis, and promote glycogen synthesis to achieve hypoglycemic effect [CK060182]. As of March 2021, this product has several experimental projects under research, of which the research and development of type I diabetes and type II diabetes is in clinical phase II, the research on glucose intolerance is in clinical phase I, and the research on metabolic disorders is in preclinical phase [CK060183].
GCGR related stable cell lines in Vitro Biotech: GCGR/CRE-Luc/HEK293 Cell Line
▍ To facilitate your GPCR research, Vitro Biotech also provides CRISPR KO cell lines for the related targets
Mouse DRD1 Knockout 4T1 cell lineHuman HTR4 Knockout A549 cell line
Mouse Glp1r Knockout B16F10 cell line
Rat Glp1r Knockout H9c2 cell line
Human GRM2 Knockout HEK293 cell line
Human CXCR2 Knockout HEK293 cell line
Human DRD2 Knockout MDA-MB-231 cell line
Mouse Lgr4 Knockout RAW 264.7 cell line
Human GLP1R Knockout THP-1 cell line
